How To Tell If The Domain Is All Real Numbers
As x tends to approach the value of the function tends to approach zero and the graph approaches the x-axis but never touches it. Co-domain All real numbers including zero.

Improve Your Math Skills By Practicing Free Problems In 39 Domain And Range 39 And Thousands Of Other Practice Lesso Exponential Functions Precalculus Math
Domain will be all numbers but 2 since the function will not be defined at 2.

How to tell if the domain is all real numbers. So if the domain of 𝑓 is all real numbers. Here the domain would be all real numbers greater than -1. Since we can only take the square root of a non-negative number the domain is all real numbers greater than or equal to 2.
Division by zero is not allowed. Co-domain All real numbers. But there are other functions.
The domain of a function is the set of all values for which the function is defined. In a graph around these points the value of y will go to infinity. We can observe that the graph extends horizontally from 5 5 to the right without bound so the domain is 5 5.
So the domain is all real numbers except 2. Domain of a Function. Domain all real numbers except 0.
That is we can find f x for all real numbers x. Hence the domain is all real x except x2 and x3. F x x x-2 x-3 here at x2 and x3 the function is not defined division by zero.
Keep in mind that if the graph continues beyond the portion of the graph we can see the domain and range may be greater than the visible values. If the domain of a function is all real numbers ie. Here the domain would be all real numbers.
Integers include the Natural numbers plus zero and all negative whole numbers. Since negative numbers and non perfect squares are not having preimage. Find the domain of f x x 2.
Since division by zero is undefined in the real number system x 2. Answer 1 of 5. That way youll be able to reasonably find the domain and range of a function just.
Rational numbers are those numbers that can be written as a fraction ab where a and b. But there are two cases where this is not always true fractions with a variable in the denominator and radicals with an even index. - D indicates that you are talking about the domain and - read as negative infinity to positive infinity is another way of saying that the domain is all real numbers.
Check whether the following function are one-to-one f. For fx x 2 the domain in interval notation is. In co-domain all real numbers are having pre-image.
A larger set of numbers are the Integers - all whole numbers. Most of the functions we have studied in Algebra I are defined for all real numbers. Fx lnx 1.
IR We could also use interval notation to assign our domain and range. The limiting factor on the domain for a rational function is the denominator which cannot be equal to zero. For example f x1x.
And the range is all real numbers except 0. There are no restrictions on x you can simply state the domain as all real numbers or use the symbol to represent all real numbers. That means 𝑥2 so the domain is all real numbers except 2.
Lets factor both the numerator and denominator. Become familiar with the shapes of basic functions like sincosine and polynomials. We can write the domain of fx in set builder notation as x x 0.
It is very important to understand. We can see from this factoring that the domain of t x is all real numbers except x. The domain and range are all real numbers because at some point the x and y values will be every real number.
The function is defined for all real numbers. So the domain of the function is the set of real numbers. It is not onto function.
First the Natural numbers are the counting numbers 12345. The domain of the function f x 1 x is all real numbers except zero since at x 0 the function is undefined. For example the domain of f x 2x 5 is because f x is defined for all real numbers x.
Secondly what does domain of all real numbers mean. Y x 12 Here when x. In mathematics the domain of a function fx is the set of all values of x that can be plugged into the function to create a defined output also known as the range of a.
As x tends to approach the function also tends to. For f x2x the domain is the set of real numbers because all real numbers can be multiplied by 2. For every member from the domain the function chooses exactly one member from the codomain.
R - 0 R defined by fx 1x. This domain is denoted. What every function actually does is simple.
The range is also all real numbers except zero. The definition of range is the set of all possible values that the function will give when we give in the domain as input. The values not included in the domain of t x are the roots of the polynomial in the denominator.
For example lets choose as a domain the set of all your Fb friends. Functions whose domains are all real numbers - YouTube. Domain -infinity infinity Range -infinity infinity.
Also as stated above the domain of a function and the range of its inverse are always the same because when we go from function to its inverse we switch the inputs and outputs. Sine functions and cosine functions have a domain of all real numbers and a range of -1 y 1. For most functions in algebra the domain is the set of all real numbers.
I have a function f x 1 x-2 where x belongs to R. When using interval notation domain and range are written as intervals of values. Note no negatives and usually no zero although some definitions have zero in the Natural numbers.
1 can not be divided by 0 hence the domain of the function f x1x is the set of real numbers WITHOUT 0. It can be literally every set.

الحلقة١شرح الرس الاول جبر اولي ث لعات Real Numbers Word Search Puzzle Vertex
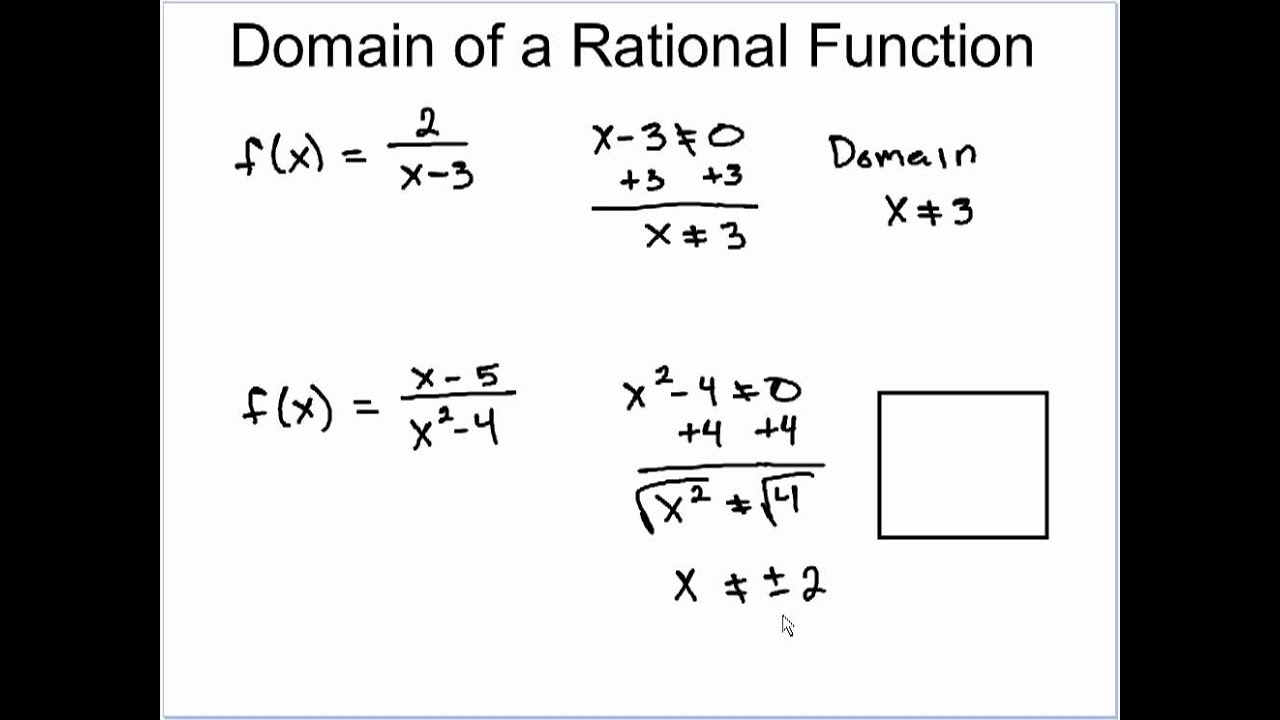
Domain Of Rational Functions Rational Function Domain Algebra

Identifying Polynomial Functions By Degrees Polynomial Functions Polynomials Real Numbers

If The Discriminant Of A Quadratic Equation Is 5 What Type Of Solutions Does The Equation Have Socratic Quadratics Quadratic Equation College Algebra Help

Tips For Teaching How To Identify Functions Teaching Middle School Math Math Lessons

Pin By Nur Jamaludin On Functions Math Functions Math Mathematics Linear Function

Function Operation Adding And Subtracting Adding And Subtracting Subtraction Real Numbers

Determining The Domain And Range For Quadratic Functions Texas Gateway In 2021 Quadratics Sat Math Quadratic Functions

If The Leading Coefficient Of A Quadratic Equation Is Positive Then The Graph Opens Upward Axis Of Quadratics Quadratic Equation Solving Quadratic Equations

4 Jpg 515 621 Pixeles Teaching Blogs Math Instruction Teaching Math

Algebra 1 Reusable Dry Erase Pocket Guides Graphing Quadratics Graphing Linear Equations Multi Step Equations Worksheets

Identifying Polynomial Functions By Degrees Polynomial Functions Polynomials Real Numbers

Practice Domain And Range Of Absolute Value Functions With Ixl 20 Free Questions Per Day Algebra 1 Absolute Value Solving Quadratic Equations
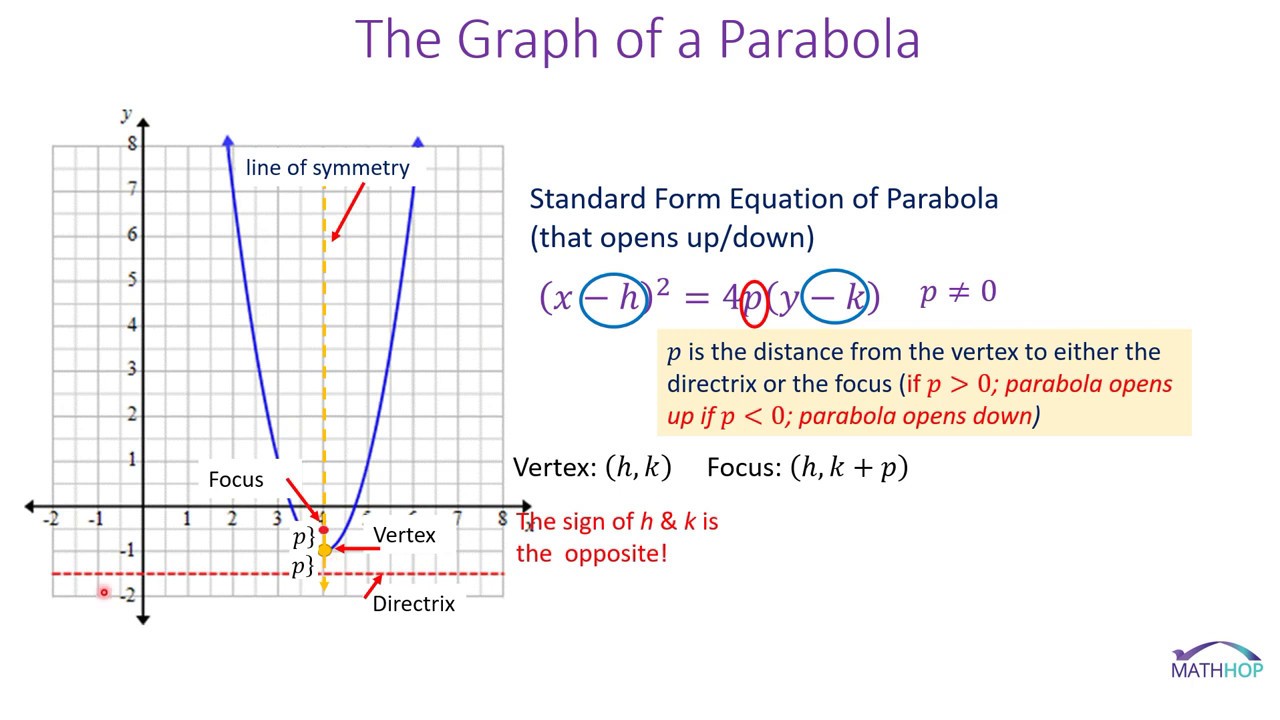
Equations And Graphs Of Parabolas Graphing Quadratics Graphing Parabolas Graphing Linear Equations
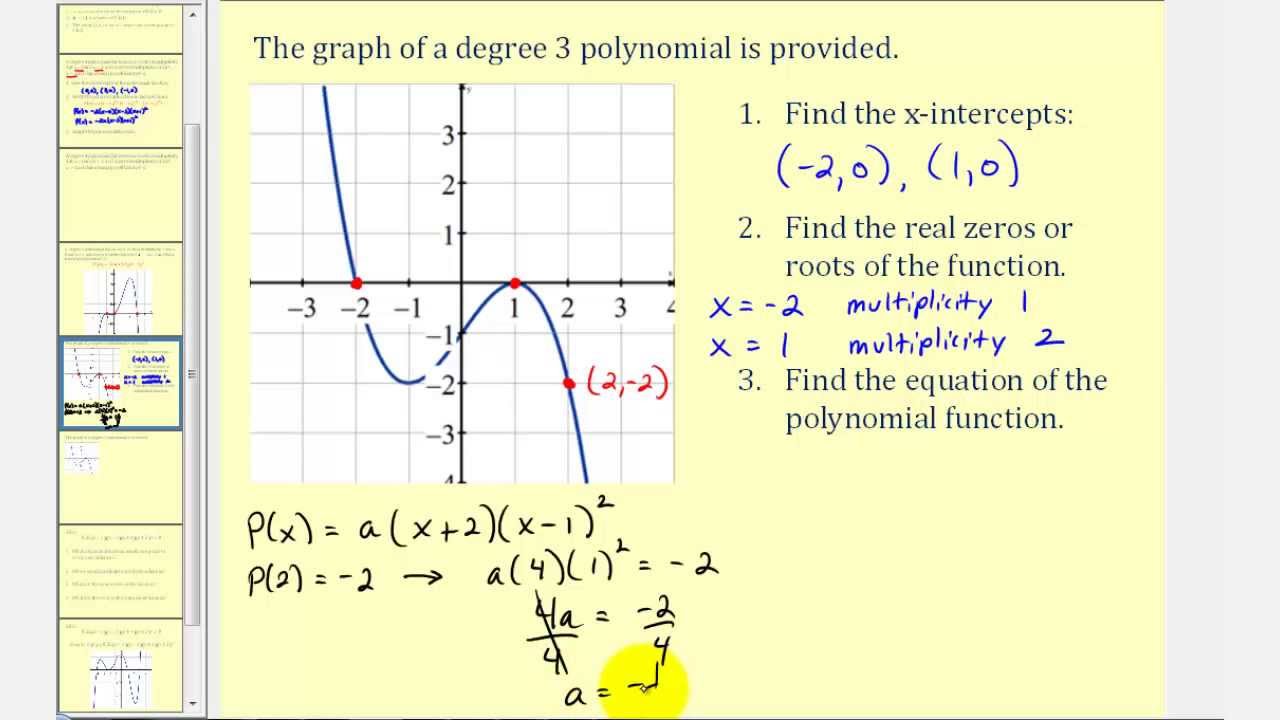
Real Zeros Factors And Graphs Of Polynomial Functions Polynomials Graphing Quadratics Graphing Linear Equations Activities

Who Am I Quadratics Solving Quadratic Equations Quadratics Practices Worksheets

Pin By Math Teacher On Algebra Quadratics Math School High School Math Classroom

Posting Komentar untuk "How To Tell If The Domain Is All Real Numbers"